在本章中,我们将安装和配置Identity框架,这只需要一点点工作.如果您转到Visual Studio并创建新的ASP.NET Core应用程序,并选择将身份验证设置为单个用户帐户的完整Web应用程序模板,则该新项目将包含为您设置的Identity框架的所有位.
我们从一个空项目开始.我们现在将从头开始设置Identity框架,这是了解完整应用程序模板中所有部分的好方法,因为如果您没有详细研究所有代码,可能会让您感到困惑./p>
首先,我们需要安装依赖项,即 Microsoft.AspNet.Identity .我们将继续安装 Microsoft.AspNet.Identity.EntityFramework ,然后实现与实体框架一起使用的Identity框架.
如果我们依赖于Identity.EntityFramework,那么该软件包将包含Identity包.
如果你构建你的拥有自己的数据存储,只需使用Identity包.
安装完依赖项后,我们可以创建一个客户用户类,其中包含我们想要的所有信息关于用户的存储.
对于这个应用程序,我们将继承Identity框架提供的类,该类将为我们提供所有必需品比如Username属性和存储散列密码的地方.
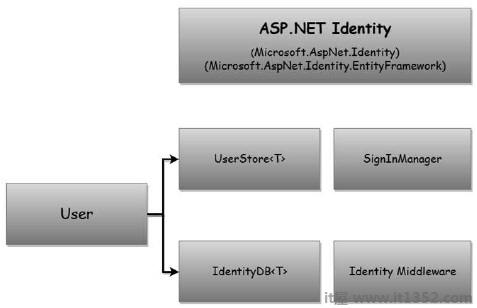
我们还需要修改 FirstAppDemoDbContext c从Identity框架的 IdentityDb 类继承.
IdentityDb为我们提供了作为用户信息与实体存储所需的一切框架.一旦我们设置了User类和 DBContext ,我们就需要使用Startup类的 ConfigureServices 方法将Identity服务配置到应用程序中.
就像我们需要添加服务来支持MVC框架一样,Identity框架需要添加到应用程序中的服务才能工作.
这些服务包括 UserStore 服务和 SignInManager 等服务.
我们将把这些服务注入我们的控制器,以便在适当的时候创建用户并发布cookie.
最后,在启动的Configure方法中,我们需要添加Identity中间件.
这个中间件不仅有助于将cookie转换为用户身份,还可以确保用户不会看不到带有401响应的空白页.
现在让我们按照下面给出的步骤.
第1步 : 我们需要继续添加对Identity框架的依赖.让我们将Microsoft.AspNet.Identity.EntityFramework依赖项添加到project.json文件中.这将包括我们需要的所有其他必要的身份包.
{
"version": "1.0.0-*",
"compilationOptions": {
"emitEntryPoint": true
},
"dependencies": {
"Microsoft.AspNet.Mvc": "6.0.0-rc1-final",
"Microsoft.AspNet.Diagnostics": "1.0.0-rc1-final",
"Microsoft.AspNet.IISPlatformHandler": "1.0.0-rc1-final",
"Microsoft.AspNet.Server.Kestrel": "1.0.0-rc1-final",
"Microsoft.AspNet.StaticFiles": "1.0.0-rc1-final",
"EntityFramework.MicrosoftSqlServer": "7.0.0-rc1-final",
"EntityFramework.Commands": "7.0.0-rc1-final",
"Microsoft.AspNet.Mvc.TagHelpers": "6.0.0-rc1-final",
"Microsoft.AspNet.Identity.EntityFramework": "3.0.0-rc1-final"
},
"commands": {
"web": "Microsoft.AspNet.Server.Kestrel",
"ef": "EntityFramework.Commands"
},
"frameworks": {
"dnx451": { },
"dnxcore50": { }
},
"exclude": [
"wwwroot",
"node_modules"
],
"publishExclude": [
"**.user",
"**.vspscc"
]
}第2步 : 保存此文件. Visual Studio会恢复包,现在我们可以添加User类.让我们通过右键单击Models文件夹并选择Add&rarr来添加User类;类.
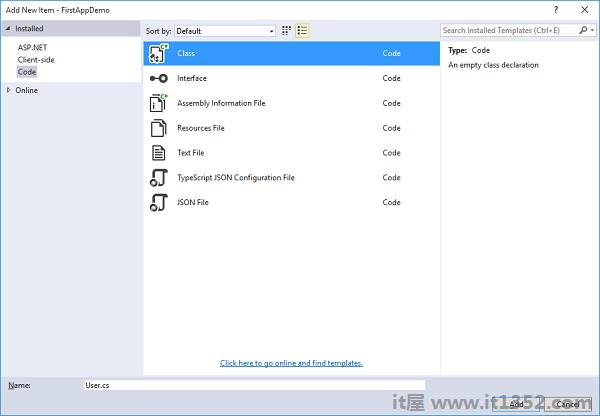
调用此类用户然后单击上面屏幕截图中的"添加"按钮.在此课程中,您可以添加属性以保存您要存储的有关用户的任何信息.
步骤3 : 让我们从Identity框架提供的类派生User类.它是Identity.EntityFramework名称空间中的IdentityUser类.
using Microsoft.AspNet.Identity.EntityFramework;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace FirstAppDemo.Models {
public class User : IdentityUser {
}
}第4步 : 现在让我们转到IdentityUser,将光标放在该符号上,然后按F12查看Visual Studio的元数据视图.
#region Assembly Microsoft.AspNet.Identity.EntityFramework, Version = 3.0.0.0,
namespace Microsoft.AspNet.Identity.EntityFramework {
public class IdentityUser : IdentityUser<string> {
public IdentityUser();
public IdentityUser(string userName);
}
}第5步 : 您可以看到IdentityUser派生自字符串的IdentityUser.您可以通过从IdentityUser派生并指定我们的泛型类型参数来更改主键的类型.您还可以使用主键存储事物,理想情况下是一个整数值.
步骤6 : 现在让我们将光标放在字符串的IdentityUser上,然后再次按F12转到元数据视图.
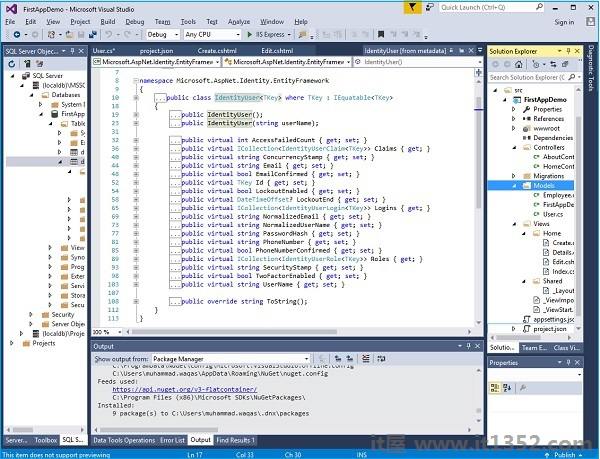
现在,您可以默认查看与用户相关的所有信息.该信息包括以下 :
我们不会在此应用程序中使用但可以使用的字段.
Identity框架可以跟踪特定用户的失败登录尝试次数,并可以在一段时间内锁定该帐户.
存储PasswordHash的字段,即PhoneNumber.我们将使用的两个重要字段是PasswordHash和UserName.
我们还将隐式使用用户的主键和ID属性.如果您需要查询特定用户,也可以使用该属性.
步骤7 : 现在,我们需要确保User包含在我们的DBContext中.那么,让我们打开我们在应用程序中的 FirstAppDemoDBContext ,而不是直接从DBContext(内置的Entity Framework基类)派生它,我们现在需要从它派生它IdentityDbContext.
using Microsoft.AspNet.Identity.EntityFramework;
using Microsoft.Data.Entity;
namespace FirstAppDemo.Models {
public class FirstAppDemoDbContext : IdentityDbContext<User> {
public DbSet<Employee> Employees { get; set; }
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder) {
optionsBuilder.UseSqlServer("Data Source = (localdb)\\MSSQLLocalDB;
Initial Catalog = FirstAppDemo;Integrated Security = True;
Connect Timeout = 30;Encrypt = False;TrustServerCertificate = True;
ApplicationIntent = ReadWrite;MultiSubnetFailover = False");
}
}
}第8步 : IdentityDbContext类也位于Microsoft.AspNet.Identity.EntityFramework命名空间中,我们可以指定它应存储的用户类型.这样,我们添加到User类的任何其他字段都会进入数据库.
IdentityDbContext带来了额外的DbSet,而不是只是为了存储用户,还有关于用户角色和用户声明的信息.
我们的用户类现已准备就绪.我们的FirstAppDemoDbContext类配置为使用Identity框架.
我们现在可以进入Configure和ConfigureServices来设置Identity框架.
第9步 : 现在让我们从 ConfigureServices 开始.除了我们的MVC服务和我们的实体框架服务,我们还需要添加我们的身份服务.这将添加Identity框架所依赖的所有服务来完成其工作.
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) {
services.AddMvc();
services.AddEntityFramework()
.AddSqlServer()
.AddDbContext<FirstAppDemoDbContext>
(option => option.UseSqlServer(Configuration["database:connection"]));
services.AddIdentity<User, IdentityRole>()
.AddEntityFrameworkStores<FirstAppDemoDbContext>();
}AddIdentity方法有两个泛型类型参数 - 类型用户实体和角色实体的类型.
两个泛型类型参数是我们用户的类型 - 我们刚创建的User类和Role类我们想要合作.我们现在将使用内置的IdentityRole.这个类位于EntityFramework命名空间中.
当我们使用带有Identity的Entity Framework时,我们还需要调用第二个方法 : AddEntityFrameworkStores.
AddEntityFrameworkStores方法将配置UserStore等服务,用于创建用户并验证其密码的服务.
第10步 : 我们需要以下两行来为应用程序配置服务.
services.AddIdentity<User, IdentityRole>() .AddEntityFrameworkStores<FirstAppDemoDbContext>();
步骤11 : 我们还需要添加中间件.我们插入中间件的位置非常重要,因为如果我们在管道中插入中间件太晚,它将永远无法处理请求.
如果我们需要授权检查在我们的MVC控制器中,我们需要在MVC框架之前插入Identity中间件,以确保成功处理cookie和401错误.
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app) {
app.UseIISPlatformHandler();
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
app.UseRuntimeInfoPage();
app.UseFileServer();
app.UseIdentity();
app.UseMvc(ConfigureRoute);
app.Run(async (context) => {
var msg = Configuration["message"];
await context.Response.WriteAsync(msg);
});
}第12步 : 我们插入中间件的位置是我们将添加Identity中间件的位置.以下是Startup.cs文件的完整实现.
using Microsoft.AspNet.Builder;
using Microsoft.AspNet.Hosting;
using Microsoft.AspNet.Http;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
using FirstAppDemo.Services;
using Microsoft.AspNet.Routing;
using System;
using FirstAppDemo.Entities;
using Microsoft.Data.Entity;
using FirstAppDemo.Models;
using Microsoft.AspNet.Identity.EntityFramework;
namespace FirstAppDemo {
public class Startup {
public Startup() {
var builder = new ConfigurationBuilder()
.AddJsonFile("AppSettings.json");
Configuration = builder.Build();
}
public IConfiguration Configuration { get; set; }
// This method gets called by the runtime.
// Use this method to add services to the container.
// For more information on how to configure your application,
// visit http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID = 398940
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) {
services.AddMvc();
services.AddEntityFramework()
.AddSqlServer()
.AddDbContext<FirstAppDemoDbContext>(option =>
option.UseSqlServer(Configuration["database:connection"]));
services.AddIdentity<User, IdentityRole>()
.AddEntityFrameworkStores<FirstAppDemoDbContext>();
}
// This method gets called by the runtime.
// Use this method to configure the HTTP request pipeline.
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app) {
app.UseIISPlatformHandler();
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
app.UseRuntimeInfoPage();
app.UseFileServer();
app.UseIdentity();
app.UseMvc(ConfigureRoute);
app.Run(async (context) => {
var msg = Configuration["message"];
await context.Response.WriteAsync(msg);
});
}
private void ConfigureRoute(IRouteBuilder routeBuilder) {
//Home/Index
routeBuilder.MapRoute("Default", "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}");
}
// Entry point for the application.
public static void Main(string[] args) => WebApplication.Run<Startup>(args);
}
}步骤13 : 现在让我们通过构建应用程序来继续前进.在下一章中,我们需要添加另一个Entity Framework迁移,以确保我们的SQL Server数据库中具有Identity模式.